Understanding the VRIO Framework: A Guide to Sustainable Competitive Advantage
In today's competitive business environment, organizations constantly strive to gain a competitive edge. Whether it's through innovation, cost leadership, or differentiation, the key question is how to sustain this advantage over time. This is where the VRIO framework comes into play.
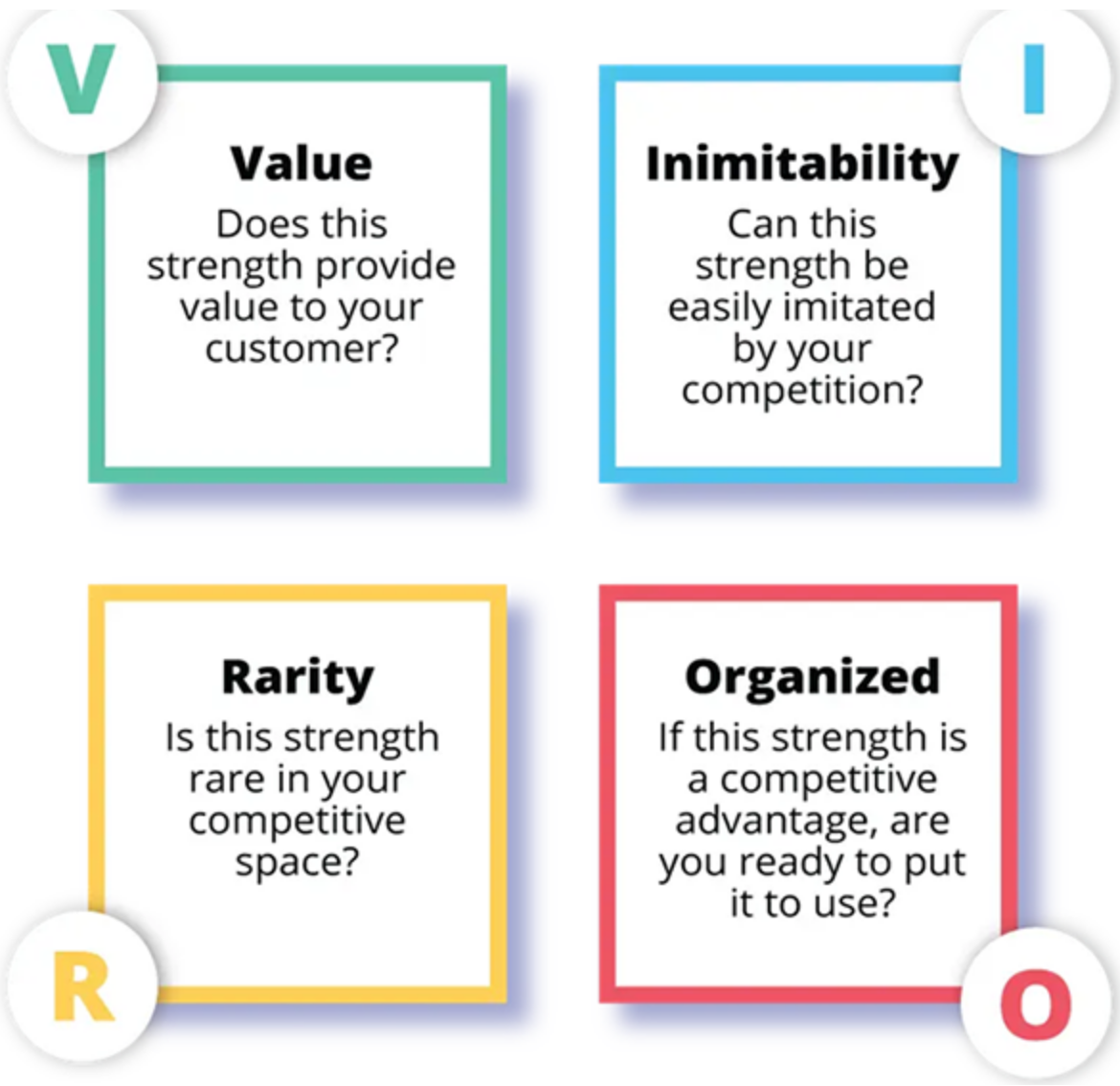
The VRIO framework, developed by Jay Barney in 1991, is a strategic tool that helps organizations assess their resources and capabilities in order to determine their potential for providing sustainable competitive advantage. VRIO stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization.
The Different Components of the VRIO
Value
The first component of the VRIO framework is value. This refers to the extent to which a resource or capability enables a firm to exploit opportunities or neutralize threats in the market. To assess the value of a resource, companies must consider whether it contributes to increased revenues, reduced costs, or improved customer satisfaction.
For example, if a company possesses cutting-edge technology that allows it to offer superior products or services, this resource would be considered valuable.
Rarity
The second component of the VRIO framework is rarity. This refers to how unique or scarce a resource or capability is in the industry. Rarity is a crucial factor in determining whether a resource can provide a sustainable competitive advantage.
Resources that are rare allow organizations to differentiate themselves from competitors and create barriers to entry. This can be achieved through patents, exclusive relationships with suppliers, or unique expertise within the organization.
Imitability
The third component of the VRIO framework is imitability. This refers to the difficulty for competitors to imitate or replicate the resource or capability. If a resource is easily replicable, it is less likely to provide a sustained competitive advantage.
Imitability can be influenced by factors such as complexity, time, and cost. For instance, if a company has invested heavily in developing a sophisticated supply chain management system, it will be challenging for competitors to imitate this capability quickly.
Organization
The final component of the VRIO framework is organization. This refers to how a firm is structured to exploit and leverage its resources and capabilities effectively. This includes factors such as leadership, culture, and coordination mechanisms.
An organization that effectively aligns its resources and capabilities with its strategic goals will be better equipped to sustain and leverage its competitive advantage.
Applying the VRIO Framework
To apply the VRIO framework, organizations should evaluate each of their resources and capabilities in terms of value, rarity, imitability, and organization. This assessment can be done through internal analysis, market research, and benchmarking against competitors.
By identifying and prioritizing resources and capabilities that meet the VRIO criteria, organizations can focus their efforts on developing sustainable competitive advantages. This may involve investing in additional resources, protecting existing ones through legal means, or leveraging organizational capabilities through strategic partnerships.
Conclusion
In today's dynamic business landscape, the VRIO framework provides organizations with a systematic approach to assess their resources and capabilities for sustained competitive advantage. By evaluating the value, rarity, imitability, and organization of each resource, companies can make informed strategic decisions and build a strong foundation for long-term success.
However, it is important to note that the VRIO framework is not a one-time analysis. Resources and capabilities are subject to change, and organizations must regularly revisit and adapt their strategies to stay ahead in the ever-evolving competitive landscape.